MyProject: Optimizing A Spacial Illumination Filter to Improve the Segmentation of Spirochaeta Bacteria
Mahish Kewalramani Kaan Sahingur
mk364@duke.edu ks447@duke.edu
| Paper PDF |
|
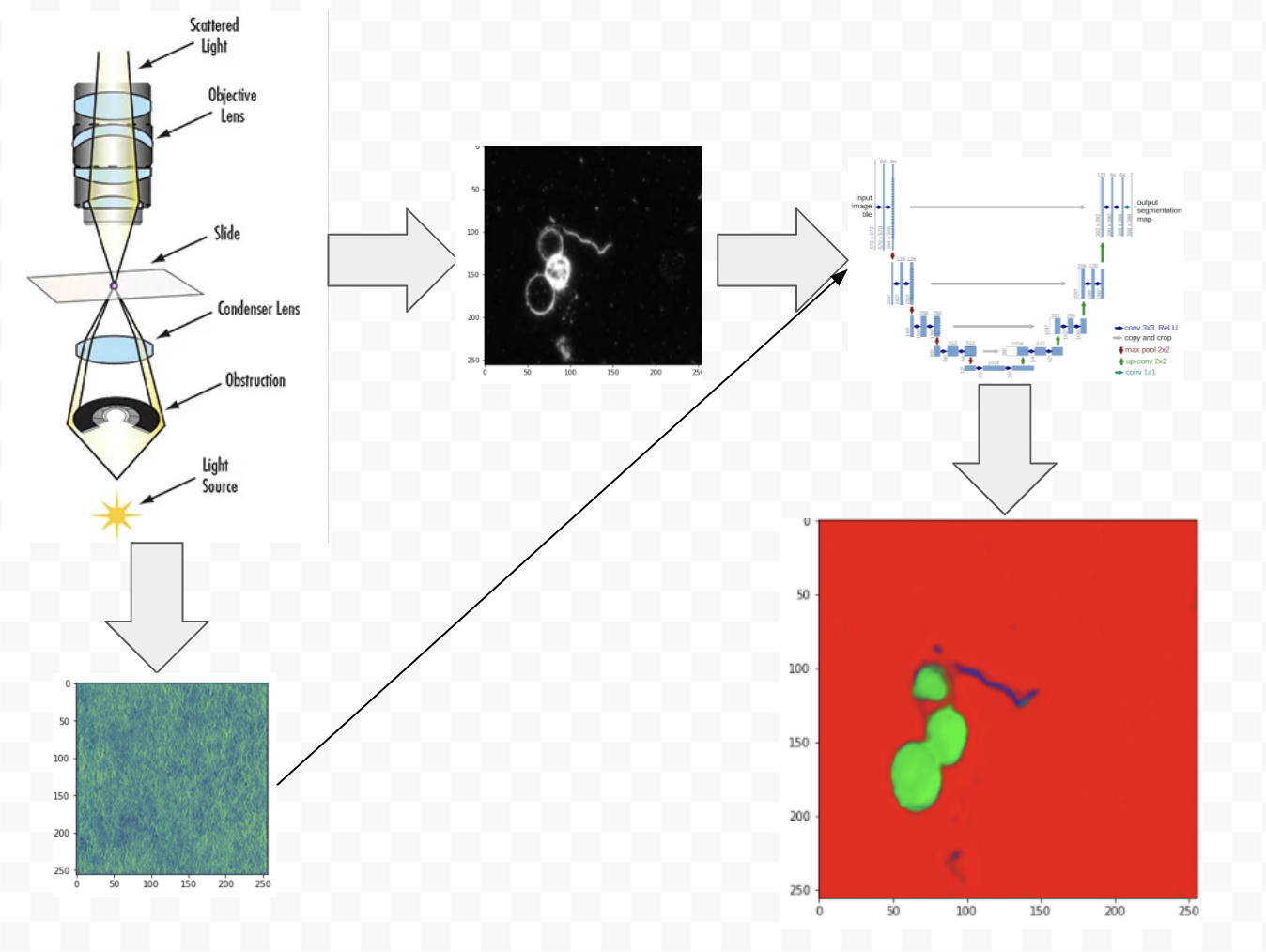
Segmentation of pathogens in blood is a vital task that is done in the biomedical community. It can provide quick insight into whether or not someone is infected by a virus or bacteria, which can help determine treatment. The present work explores the addition of a physical layer over a commonly used deep neural network for segmentation tasks, the U-Net, to build a model that can yield better results. The results show that the model with a physical layer does not do much better in segmenting the data. That being said, the model with the physical layer does not over fit to the train data as much, indicating promising results of including a physical layer in imaging blood samples. |
|
|
| Paper: |
Code and Data:
|