Optics + Algorithms for better biology
Research at the intersection of biomedical optics,
machine learning and algorithm design.
At the Computational Optics Lab at Duke University, we develop cutting-edge microscopes, cameras, and algorithms to improve biomedical imaging. Led by Dr. Roarke Horstmeyer, our team combines biomedical optics, machine learning, and computational imaging to capture clearer, more detailed images of biological structures. We're passionate about pushing the boundaries of imaging technology and sharing our discoveries with the world.
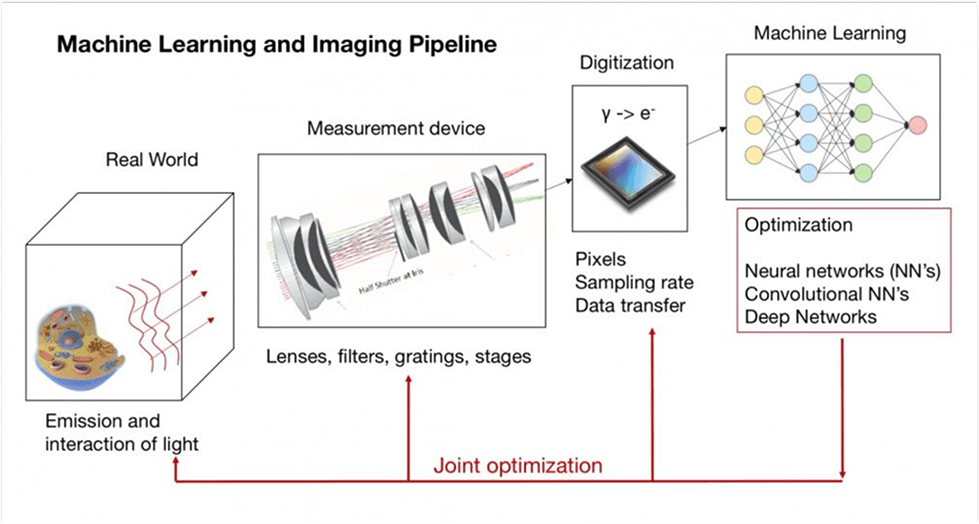
Machine Learning and Imaging Class
Dr. Horstmeyer currently teaches BME548: Machine Learning and Imaging.
Recordings of the course are available on our lab's YouTube Channel.
Dr. Horstmeyer also teaches Duke's first year design course Engineering 101.